Le revisioni sistematiche (RS) degli studi di accuratezza diagnostica sono spesso caratterizzate da risultati notevolmente eterogenei conseguenti alle differenze di pianificazione e conduzione degli studi inclusi, dei quali è fondamentale valutare la qualitĂ . Dalla sua pubblicazione nel 2003, lo strumento QUADAS (Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies) è stato ampiamente utilizzato (1,2). Oltre 200 abstract inseriti nel Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects menzionano questo strumento, citato piĂš di 500 volte. LâAgency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ), la Cochrane Collaboration (3) e il National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) ne raccomandano lâutilizzo per condurre RS degli studi di accuratezza diagnostica.
Lo strumento QUADAS originale comprende 14 item che valutano il rischio di bias, le fonti di variabilitĂ (applicabilitĂ ) e la qualitĂ del reporting: per ogni item occorre indicare âsĂŹâ, ânoâ o ânon chiaroâ (1). Grazie a nuove evidenze, esperienza degli autori, report degli utilizzatori e feedback della Cochrane Collaboration sono state suggerite aree di potenziale miglioramento. In particolare, gli utilizzatori del QUADAS hanno riportato criticitĂ relative alla valutazione di alcuni item (es. spettro dei pazienti, risultati dei test non interpretabili o intermedi e whithdrawals); alla possibile sovrapposizione tra item (es. bias di verifica parziale e whithdrawals); alle situazioni in cui QUADAS è difficile da utilizzare (es. quando lo standard di riferimento richiede il follow-up dei pazienti).
Questo articolo descrive QUADAS-2, versione aggiornata dello strumento.
METODI
Lo sviluppo di QUADAS-2 è basato sullâapproccio a 4 step proposto da Moher et coll. (4): definizione dellâobiettivo, revisione delle evidenze, meeting di consenso e test pilota al fine di perfezionare lo strumento.
Definizione dellâobiettivo. Un comitato direttivo di 9 esperti nel campo della ricerca diagnostica, molti dei quali avevano partecipato allo sviluppo dello strumento originale, ha definito le caratteristiche principali di QUADAS-2. Innanzitutto, il concetto di âqualitĂ â è stato separato in due dimensioni: ârischio di biasâ e âproblemi di applicabilitĂ â. La qualitĂ degli studi di accuratezza diagnostica è stata definita sia in termini di rischio di bias che di problemi di applicabilitĂ di uno studio, valutando in particolare se: 1) le stime di accuratezza diagnostica hanno evitato il rischio di bias; 2) gli studi primari sono applicabili al quesito della RS. Il bias si verifica quando errori sistematici nel disegno o nella conduzione di uno studio ne distorcono i risultati. Uno studio primario può avere unâapplicabilitĂ limitata alla popolazione in studio se, rispetto al quesito definito dalla RS, arruola partecipanti con differenti caratteristiche demografiche o cliniche, se il test in studio viene applicato o interpretato in modo diverso o se la definizione della condizione target è differente.
Nel QUADAS-2, la riduzione del numero di domini principali è finalizzata a minimizzare le sovrapposizioni e ad estendere lo strumento alla valutazione sia di studi comparativi tra diversi test diagnostici, sia di studi che prevedono standard di riferimento basati sul follow-up, fatta espressa esclusione degli studi che valutano fattori prognostici.
Ă stato inoltre proposto di modificare la valutazione sĂŹ/no/non chiaro del QUADAS originale in âbasso rischio di biasâ o âelevato rischio di biasâ, analogamente allo strumento sviluppato dalla Cochrane Collaboration per valutare il rischio di bias nei trial clinici. Infatti, un giudizio esplicito sul rischio di bias è piĂš informativo e i feed-back relativi allo strumento Cochrane per classificare il rischio di bias hanno suggerito che la classificazione sĂŹ/no/non chiaro era fuorviante (5).
Revisione delle evidenze. Durante lo sviluppo di QUADAS-2 sono state condotte 4 revisioni (6). La prima ha indagato le modalitĂ di valutare e integrare la qualitĂ in 54 RS di accuratezza diagnostica pubblicate tra il 2007 e il 2009. La seconda revisione ha utilizzato un questionario web-based per raccogliere un feedback strutturato da 64 autori di RS che avevano utilizzato QUADAS. La terza revisione condotta su 101 studi ha permesso di aggiornare le fonti di bias e di variabilitĂ negli studi di accuratezza diagnostica (7). La quarta revisione ha esaminato 8 studi che hanno valutato QUADAS: i dati completi saranno oggetto di unâulteriore pubblicazione. Le evidenze emerse da queste revisioni hanno informato le decisioni sugli argomenti oggetto di discussione nel meeting di consenso. Sono stati sintetizzati i problemi riportati con lo strumento QUADAS originale, le evidenze per ciascun item originale e definiti i possibili item aggiuntivi relativi a bias e applicabilitĂ . è stato inoltre redatto un elenco di ulteriori item candidati per la valutazione di studi di confronto tra differenti test in studio.
Meeting di consenso. Il 21 settembre 2010 a Birmingham (UK) si è svolto il meeting per sviluppare la prima bozza di QUADAS-2. I 24 partecipanti del gruppo QUADAS-2 erano esperti metodologi e revisori che lavorano sulle RS di accuratezza diagnostica. Sono state presentate sintesi delle evidenze scientifiche e i partecipanti sono stati divisi in piccoli gruppi per discutere dei contenuti dello strumento (protocollo del test, procedure di verifica, interpretazione, analisi, selezione dei pazienti o disegno dello studio, item di valutazione comparativa tra test), dellâapplicabilitĂ e delle decisioni concettuali. Sulla base dei risultati concordati nel meeting, i membri del comitato direttivo hanno prodotto la prima bozza di QUADAS-2.
Test pilota e perfezionamento. Successivamente lo strumento QUADAS-2 è stato perfezionato attraverso vari round di test pilota. Ad ogni round erano previsti questionari online per raccogliere feedback strutturati, ma sono stati accettati anche feedback verbali o via e-mail. I test pilota sono stati condotti dai membri del gruppo QUADAS-2, dai partecipanti al Cochrane Colloquium a Keystone (Colorado, ottobre 2010), da esperti di RS presenti al tavolo tecnico del NICE e da studenti svizzeri in scienze biomediche.
Il QUADAS-2 è stato sperimentato da coppie di revisori in 5 RS relative a diversi argomenti. La riproducibilitĂ tra osservatori variava in maniera considerevole e câera maggiore accordo sullâapplicabilitĂ che sul rischio di bias. Unâulteriore coppia di revisori esperti ha testato lo strumento su una RS con test in studio multipli. Il feedback di questi revisori ha mostrato una scarsa riproducibilitĂ tra osservatori e alcuni problemi nellâapplicazione del dominio sullâaccuratezza comparativa degli studi.
Tenendo conto di queste problematiche e della limitate evidenze sul rischio di bias e sulle fonti di variabilità in questi studi, QUADAS-2 non prevede criteri per valutare gli studi che confrontano test multipli. Il feedback relativo a tutte le altre fasi del processo è stato positivo: in particolare, tutti i partecipanti hanno preferito QUADAS-2 allo strumento originale.
Ruolo dei finanziatori. Questo articolo è stato finanziato da: Medical Research Council, National Institute for Health Research, Cancer Research UK e Netherlands Organization for Scientific Research (916.10.034). Gli sponsor non hanno avuto alcun ruolo nel disegno dello studio, nella raccolta, analisi e interpretazione dei dati, nella stesura del report o nella decisione di sottomettere il manoscritto per la pubblicazione.
QUADAS-2
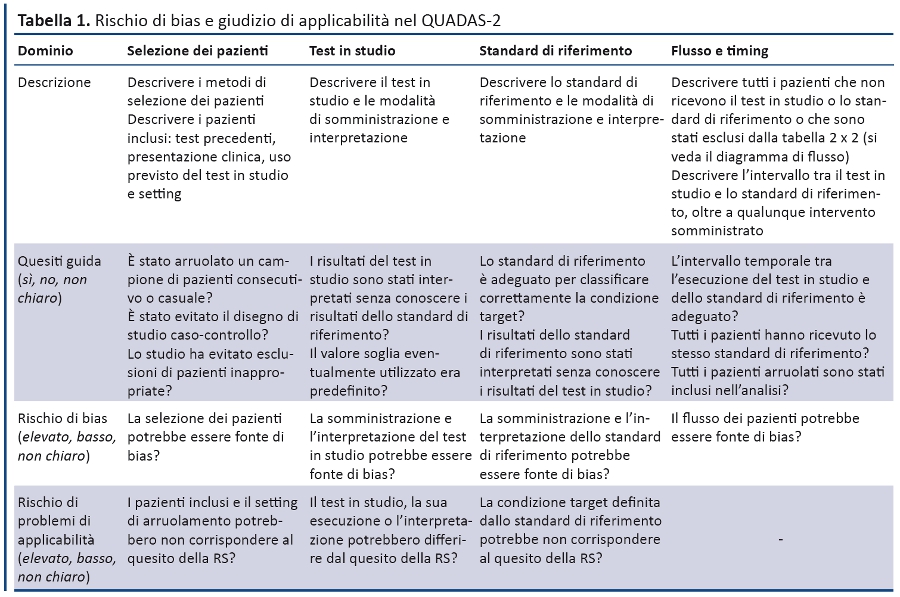
Lo strumento QUADAS-2 è stato progettato per valutare la qualitĂ degli studi di accuratezza diagnostica e dovrebbe essere utilizzato in aggiunta allâestrazione dei dati (es. disegno dello studio, risultati, etc.) da utilizzare nella RS. QUADAS-2 è strutturato in 4 domini: selezione dei pazienti, test in studio, standard di riferimento e flusso dei pazienti e timing di test in studio e standard di riferimento (tabella 1).
Lâutilizzo dello strumento prevede quattro fasi: 1) esplicitare il quesito della RS; 2) definire precise istruzioni per la RS; 3) rivedere il diagramma di flusso pubblicato nello studio primario o costruirlo se non riportato; 4) valutare bias e applicabilitĂ . Ogni dominio viene valutato in termini di rischio di bias e i primi 3 anche in relazione allâapplicabilitĂ . Per aiutare a valutare il rischio di bias, QUADAS-2 fornisce quesiti guida correlati ai potenziali bias dello studio.
Fase 1. Quesito della RS
I revisori devono anzitutto descrivere il quesito della RS in termini di pazienti, test in studio, standard di riferimento e condizione target. Considerato che lâaccuratezza di un test può dipendere dal setting in cui sarĂ utilizzato nel percorso diagnostico, i revisori devono inoltre descrivere i pazienti in termini di setting, lâuso previsto del test in studio, le caratteristiche dei pazienti e lâesecuzione di eventuali test precedenti (8,9).
Fase 2. Adattamento specifico alla revisione
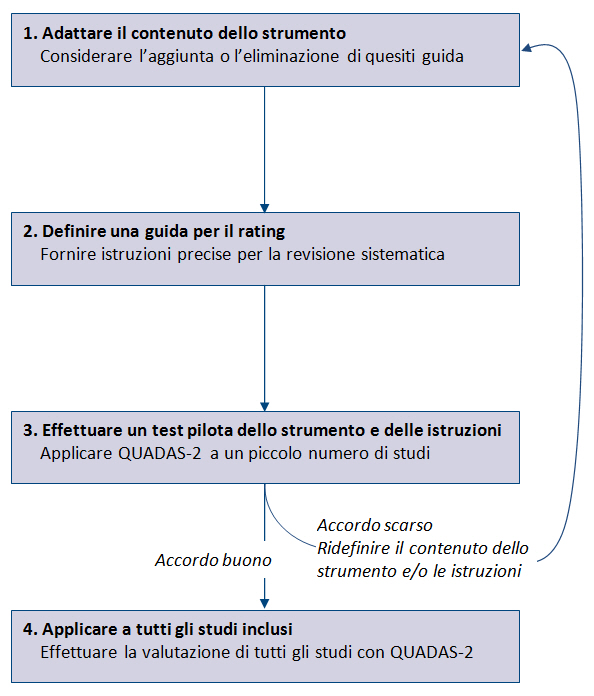
È fondamentale adattare QUADAS-2 a ciascuna RS, aggiungendo o eliminando quesiti guida e sviluppando precise istruzioni per valutare ciascun quesito guida e usare questa informazione per stimare il rischio di bias (figura 1). Come primo step occorre considerare se uno o piĂš quesiti guida non possono essere applicati alla RS o se specifiche caratteristiche della RS non sono adeguatamente affrontati dai quesiti guida. Ad esempio, se una RS valuta lâaccuratezza di un test diagnostico ad interpretazione oggettiva, può essere eliminato il quesito guida relativo al blinding di chi interpreta i risultati del test in studio rispetto allo standard di riferimento. Gli autori della RS dovrebbero evitare di aggiungere troppi quesiti guida per non rendere troppo complesso lo strumento. Una volta definito il contenuto, è necessario definire precise istruzioni per il rating della RS. Lo strumento dovrebbe essere testato in maniera indipendente da almeno due persone; se la concordanza è buona, lo strumento può essere utilizzato per valutare tutti gli studi inclusi, altrimenti può rendersi necessario un ulteriore affinamento.
Fase 3. Diagramma di flusso
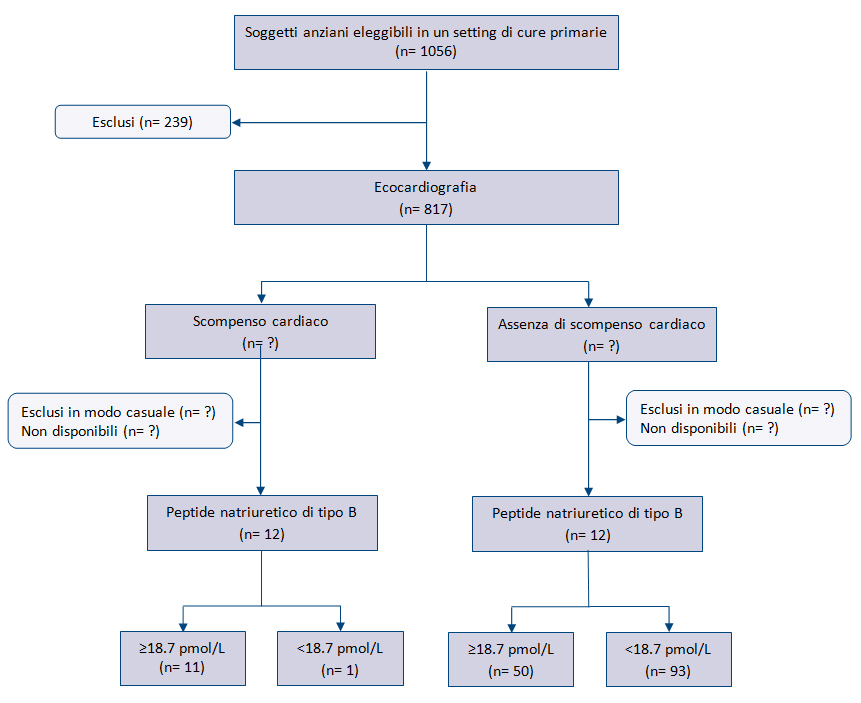
Lo step successivo consiste nel rivedere il diagramma di flusso dello studio primario o costruirlo se non è riportato o inadeguato. Il diagramma di flusso faciliterĂ la valutazione del rischio di bias e dovrebbe fornire informazioni sul metodo di reclutamento dei pazienti (es. serie consecutiva di pazienti con sintomi specifici che fanno sospettare la condizione di interesse, oppure su casi e controlli), la sequenza di esecuzione del test e il numero di pazienti sottoposti al test in studio e allo standard di riferimento. Il diagramma di flusso può essere disegnato a mano perchĂŠ questo step non deve essere riportato nella valutazione con QUADAS-2. La figura 2 riporta lâesempio di un diagramma di flusso relativo a uno studio primario che ha valutato lâaccuratezza diagnostica del peptide natriuretico di tipo B per la diagnosi di scompenso cardiaco.
Fase 4. Valutazione del rischio di bias e dellâapplicabilitÀ
Rischio di bias. La prima parte di ogni dominio riguarda i bias e comprende tre sezioni: informazioni utilizzate per valutare il rischio di bias, quesiti guida e valutazione del rischio di bias. Registrando le informazioni utilizzate per la valutazione (âsupporto alla valutazioneâ), si è cercato di renderla trasparente e di facilitare la discussione tra i revisori che effettuano le valutazioni in maniera indipendente (5). I quesiti guida aggiuntivi aiutano a formulare un giudizio: la risposta può essere âsĂŹâ, ânoâ, ânon chiaroâ, tenendo conto che âsĂŹâ corrisponde a un basso rischio di bias.
Il rischio di bias viene giudicato come âbassoâ, âelevatoâ o ânon chiaroâ. Se a tutti i quesiti guida relativi ad un dominio è stato risposto âsĂŹâ, il rischio di bias può essere ritenuto âbassoâ. Se ad ogni quesito guida è stato risposto ânoâ questo evidenzia un rischio potenziale di bias. I revisori, quindi, devono utilizzare le istruzioni sviluppate nella fase 2 per stimare il rischio di bias. La categoria ânon chiaroâ dovrebbe essere usata solo quando i dati riportati sono insufficienti per consentire una valutazione.
ApplicabilitĂ . Le sezioni relative allâapplicabilitĂ sono strutturate in modo analogo a quelle dei bias, ma non includono i quesiti guida. I revisori devono registrare le informazioni su cui viene basato il giudizio di applicabilitĂ ed esprimere le loro perplessitĂ quando il disegno dello studio non corrisponde al quesito della RS. Il rischio di problemi di applicabilità è classificato come âbassoâ, âelevatoâ, ânon chiaroâ. Le valutazioni sullâapplicabilitĂ dovrebbero sempre fare riferimento alla prima fase che riporta il quesito della RS. Anche in questo caso la categoria ânon chiaroâ dovrebbe essere utilizzata quando i dati riportati sono insufficienti. Le sezioni successive forniscono per ciascun dominio del QUADAS-2 una spiegazione sintetica dei quesiti guida per valutare il rischio di bias e i problemi di applicabilitĂ .
Dominio 1. Selezione dei pazienti
Rischio di bias: la selezione dei pazienti potrebbe essere fonte di bias?
Quesito guida 1. È stato arruolato un campione consecutivo o casuale di pazienti?
Quesito guida 2. È stato evitato un disegno di studio caso-controllo?
Quesito guida 3. Lo studio ha evitato esclusioni di pazienti inappropriate?
Uno studio di accuratezza diagnostica dovrebbe idealmente arruolare un campione consecutivo, o casuale, di pazienti eleggibili con il sospetto di malattia, per evitare potenziali bias. Gli studi che effettuano esclusioni inappropriate, ad esempio escludendo pazienti âdifficili da diagnosticareâ possono determinare stime di accuratezza diagnostica troppo ottimistiche. Ad esempio, in una RS sugli anticorpi anti-CCP per la diagnosi di artrite reumatoide, alcuni studi hanno arruolato pazienti consecutivi con diagnosi confermate. Questi studi hanno mostrato una maggiore sensibilitĂ del test anti-CCP rispetto ad altri che includevano sia pazienti con sospetta malattia, ma nei quali la diagnosi non era stata confermata, sia quelli âdifficili da diagnosticareâ (10). Analogamente, gli studi che arruolano pazienti con malattia nota e un gruppo di controllo senza la condizione target possono sovrastimare lâaccuratezza diagnostica (7,11). Lâesclusione di pazienti con segnali di allarme (red flags) per la condizione target, che possono essere piĂš facili da diagnosticare, può invece sottostimare lâaccuratezza diagnostica.
ApplicabilitĂ : pazienti inclusi e setting di arruolamento potrebbero non corrispondere al quesito della RS?
Problemi di applicabilitĂ si possono verificare se i pazienti inclusi nello studio sono diversi rispetto a quelli previsti dal quesito della RS, in termini di gravitĂ della condizione target, caratteristiche demografiche, presenza di diagnosi differenziali o comorbiditĂ , setting dello studio e precedenti protocolli di test. Ad esempio, tumori di maggiori dimensioni, rispetto a quelli piĂš piccoli, sono piĂš facilmente identificabili con i test di imaging e infarti del miocardio piĂš estesi, rispetto a quelli piĂš circoscritti, determinano livelli piĂš elevati di enzimi cardiaci rispetto. Di conseguenza una loro piĂš frequente identificazione aumenta la sensibilitĂ dei test (3).
Dominio 2. Test in studio
Rischio di bias: lâesecuzione o lâinterpretazione del test in studio potrebbe essere fonte di bias?
Quesito guida 1. I risultati del test in studio sono stati interpretati senza conoscere i risultati dello standard di riferimento?
Questo item è simile alla definizione di blinding negli studi sperimentali: infatti, lâinterpretazione del test in studio può essere influenzata dalla conoscenza dei risultati dello standard di riferimento (7). Il potenziale bias è causato dalla soggettivitĂ interpretativa del test in studio e dalla sequenza temporale. Se il test in studio è sempre eseguito e interpretato prima dello standard di riferimento, la risposta al quesito è affermativa.
Quesito guida 2. Il valore soglia eventualmente utilizzato è stato predefinito?
La selezione di un valore soglia del test per ottimizzare sensibilità e/o specificità può determinare performance del test eccessivamente ottimistiche, che rischiano di essere piÚ deboli in un campione indipendente di pazienti in cui viene utilizzato lo stesso valore soglia (12).
ApplicabilitĂ : il test in studio, la sua esecuzione o interpretazione potrebbero differire dal quesito della RS?
Le differenze relative alla tecnologia diagnostica, la sua esecuzione o interpretazione possono influenzarne le stime di accuratezza diagnostica. Se i metodi del test in studio variano rispetto a quelli definiti dal quesito della RS, possono esserci problemi di applicabilitĂ . Ad esempio, un trasduttore a ultrasuoni ad elevata frequenza aumenta la sensibilitĂ per valutare i pazienti con trauma addominale (13).
Dominio 3. Standard di riferimento
Rischio di bias: lo standard di riferimento, la sua conduzione o interpretazione potrebbero essere fonte di bias?
Quesito guida 1. Lo standard di riferimento è adeguato per classificare correttamente la condizione target?
Considerato che le stime di accuratezza dei test si basano sul presupposto che lo standard di riferimento abbia sensibilitĂ e specificitĂ del 100%, si assume che le differenze rilevate tra risultati del test in studio e quelli dello standard di riferimento siano conseguenti a una minore accuratezza diagnostica del test in studio (14,15).
Quesito guida 2. I risultati dello standard di riferimento sono stati interpretati senza conoscere i risultati del test in studio?
Il quesito è simile a quello relativo allâinterpretazione del test in studio: il potenziale bias può originare dal conoscere il risultato dello standard di riferimento (7).
ApplicabilitĂ : la condizione target definita dallo standard di riferimento potrebbe non corrispondere al quesito della RS?
Lo standard di riferimento può non essere affetto da bias, ma la condizione target che identifica può differire da quella prevista dal quesito della RS. Ad esempio, quando si definisce lâinfezione delle vie urinarie lo standard di riferimento è generalmente basato sullâurinocoltura, ma il valore soglia di positivitĂ può variare (16).
Dominio 4. Flusso e timing
Rischio di bias. Il flusso di pazienti potrebbe essere fonte bias?
Quesito guida 1. Lâintervallo temporale tra lâesecuzione del test in studio e dello standard di riferimento è adeguato?
Idealmente i risultati del test in studio e dello standard di riferimento dovrebbero essere ottenuti sugli stessi pazienti nello stesso momento. In caso di ritardo, oppure se tra lâesecuzione del test in studio e lo standard di riferimento è stato iniziato un trattamento, può verificarsi unâerrata classificazione dei pazienti conseguente al miglioramento/peggioramento della condizione target. La durata dellâintervallo può determinare un elevato rischio di bias che varia in relazione alla condizione target: ad esempio un ritardo di un paio di giorni può non essere un problema per le malattie croniche, mentre per le malattie infettive acute anche un breve ritardo può essere rilevante. Viceversa, se lo standard di riferimento richiede un periodo di follow-up, questo deve essere sufficientemente lungo per valutare la presenza/assenza della condizione target. Ad esempio, per valutare lâaccuratezza diagnostica della risonanza magnetica nella diagnosi precoce della sclerosi multipla, è necessario un follow-up di almeno 10 anni per essere certi che tutti i pazienti soddisfino i criteri diagnostici per la sclerosi multipla (17).
Quesito guida 2. Tutti i pazienti hanno ricevuto lo stesso standard di riferimento?
Il bias di verifica (verification bias) avviene quando non tutti i pazienti hanno una conferma diagnostica con lo stesso standard di riferimento. Se i risultati del test in studio condizionano la decisione sullo standard di riferimento da utilizzare o utilizzato, lâaccuratezza diagnostica può essere soggetta a bias (11,18). Ad esempio, uno studio che ha valutato lâaccuratezza del D-dimero per la diagnosi di embolia polmonare, ha effettuato la scintigrafia ventilatoria-perfusoria (standard di riferimento 1) nei soggetti positivi al test e utilizzato solo un follow-up clinico nei soggetti con test negativo (standard di riferimento 2). Questo può comportare lâerrata classificazione di alcuni falsi negativi come veri negativi: pazienti con embolia polmonare negativi al test in studio, se persi al follow-up, possono essere classificati come soggetti senza embolia polmonare, determinando una sovrastima di sensibilitĂ e specificitĂ .
Quesito guida 3. Tutti i pazienti arruolati sono stati inclusi nellâanalisi?
Tutti i pazienti arruolati nello studio dovrebbero essere inclusi nellâanalisi (19), visto che la discrepanza tra il numero di pazienti arruolati e quelli inclusi nella tabella 2x2 dei risultati è fonte di potenziale bias. Ad esempio, i pazienti persi al follow-up differiscono sistematicamente da quelli che rimangono nello studio.
Integrare le valutazioni dI QUADAS-2 nelle REVISIONI SISTEMATICHE degli studi di accuratezza diagnostica
QUADAS-2 non dovrebbe essere usato per generare uno âscore di qualitĂ â cumulativo, a causa delle criticitĂ ben note con questi score (20,21). Se ad uno studio viene assegnato lo score come âbassoâ rispetto a tutte le sezioni relative ai bias o allâapplicabilitĂ , è opportuno formulare una valutazione complessiva di âbasso rischio di biasâ o âlimitati problemi di applicabilitĂ â. Se uno studio è giudicato a rischio âelevatoâ o ânon chiaroâ su una o piĂš sezioni, allora può essere giudicato âa rischio di biasâ o âcon problemi di applicabilitĂ â.
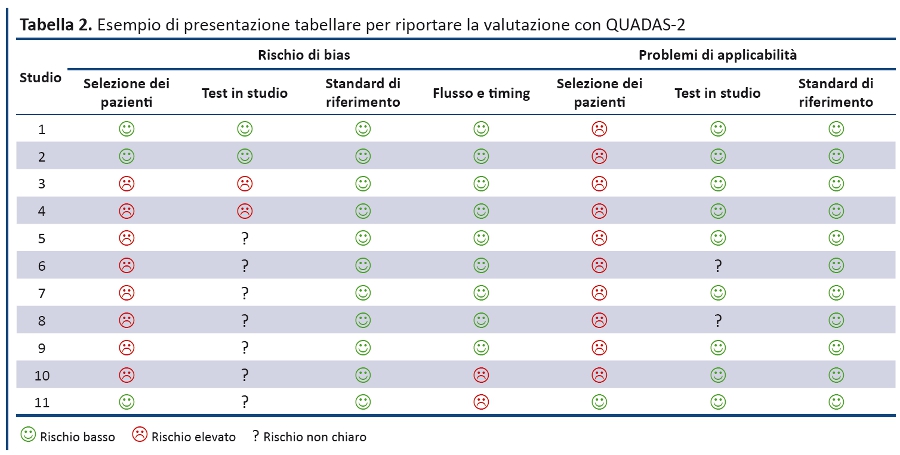
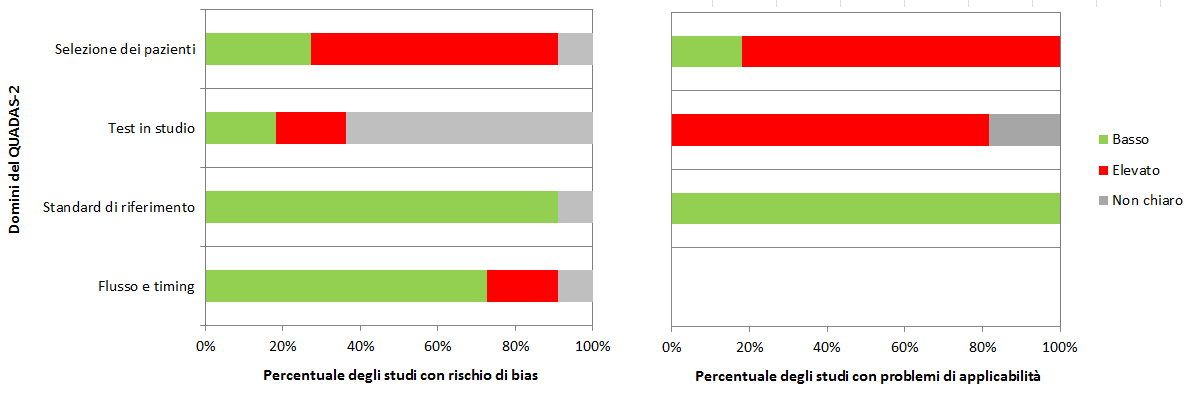
Le RS dovrebbero prevedere almeno una sintesi dei risultati della valutazione con QUADAS-2 per tutti gli studi inclusi, ovvero il numero di studi per i quali il rischio di bias e di problemi di applicabilitĂ per ciascun dominio è stato valutato âbassoâ, âelevatoâ o ânon chiaroâ. I revisori possono scegliere di evidenziare gli studi in cui hanno dato costantemente una valutazione positiva o negativa rispetto a specifici quesiti guida. La tabella 2 e la figura 3 riportano esempi su come presentare in maniera sintetica le valutazioni con QUADAS-2.
I revisori possono scegliere di restringere lâanalisi primaria cosĂŹ da includere solo gli studi a basso rischio di bias e/o con limitati problemi di applicabilitĂ . Può essere appropriato restringere lâinclusione degli studi nella RS in relazione a criteri omogenei, ma spesso è preferibile esaminare tutte le evidenze rilevanti per poi individuare possibili cause di eterogeneitĂ (17,22). Unâanalisi per sottogruppi e/o di sensibilitĂ tra gli studi può essere condotta per documentare la variazione delle stime sullâaccuratezza diagnostica del test in studio rispetto a un rischio di bias elevato, basso o non chiaro. I domini o i quesiti guida possono essere inclusi come item in unâanalisi di meta-regressione, per valutare la loro associazione rispetto allâaccuratezza stimata.
Il sito web QUADAS (www.quadas.org) contiene lo strumento QUADAS-2, informazioni sul training, una banca di quesiti guida aggiuntivi, una guida piĂš dettagliata per ogni sezione, esempi di valutazioni completate con QUADAS-2 e risorse scaricabili, tra cui un database Microsoft Access per lâestrazione dei dati, un foglio Excel per la produzione di presentazioni grafiche dei risultati e modelli di tabelle in Word per la sintesi dei risultati.
DISCUSSIONE
Lâattenta valutazione della qualitĂ degli studi inclusi è fondamentale per condurre RS degli studi di accuratezza diagnostica. È stato utilizzato un rigoroso processo evidence-based per sviluppare lo strumento QUADAS-2 dal QUADAS, giĂ ampiamente utilizzato. Lo strumento QUADAS-2 offre elementi aggiuntivi e perfezionati, inclusa la distinzione tra bias e applicabilitĂ . Individua 4 domini chiave supportati da quesiti guida per facilitare la valutazione e la classificazione del rischio di bias, i problemi di applicabilitĂ e le modalitĂ di valutazione degli studi che prevedono il follow-up come standard di riferimento.
QUADAS-2 rappresenta una notevole evoluzione dello strumento originale: sarebbe auspicabile estendere QUADAS-2 per consentire la valutazione di studi che confrontano piÚ test in studio, ma le evidenze scientifiche in questo ambito sono ancora insufficienti ed è necessario pianificare ulteriori ricerche. Auspicando che QUADAS-2 aiuti a sviluppare una robusta evidence-base per test e procedure diagnostiche, sono benvenuti commenti e feedback tramite il sito web QUADAS.
Strumenti
Strumento QUADAS-2
Template per la presentazione grafica
QUADAS-2 Database